Understanding Various Kinds of Skin Pigmentation
- brandelitedevteam
- Aug 7
- 4 min read
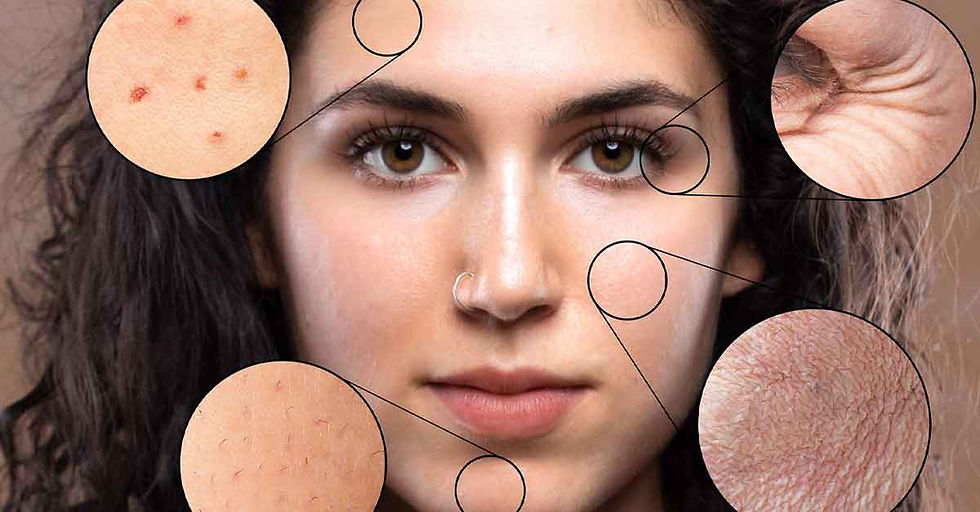

Skin pigmentation is a natural phenomenon that gives our skin its unique color and tone. However, when pigmentation becomes uneven or develops irregularly, it can become a cosmetic concern for many individuals. Understanding the types of skin pigmentation and their underlying mechanisms is crucial for anyone dealing with these conditions.
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is primarily determined by melanin production in specialized cells called melanocytes. When these cells produce melanin unevenly or in excess, various pigmentation disorders can occur, affecting both appearance and self-confidence.
Types of Skin Pigmentation
Melasma
Melasma appears as brown or gray patches, typically on the face, forehead, cheeks, and upper lip. This condition is commonly known as the "pregnancy mask" due to its frequent occurrence during pregnancy.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH develops after skin inflammation or injury, leaving dark spots where acne, cuts, or other skin trauma once occurred. This type is particularly common in individuals with darker skin tones.
Solar Lentigines (Age Spots)
Also called liver spots or sun spots, these flat, brown spots appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and shoulders. They're primarily caused by cumulative sun exposure over time.
Vitiligo
Unlike other pigmentation disorders, vitiligo causes loss of pigmentation, resulting in white patches on the skin. This autoimmune condition affects melanocyte function, leading to depigmented areas.
Café-au-lait Spots
These light brown birthmarks are usually present from birth or develop in early childhood. While generally harmless, multiple spots may indicate underlying genetic conditions.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Understanding the causes of skin pigmentation is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Multiple factors contribute to pigmentation disorders:
Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet radiation is the primary trigger for many pigmentation issues. UV rays stimulate melanin production as a protective mechanism, but excessive exposure can lead to uneven pigmentation and age spots.
Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma and other pigmentation changes. Estrogen and progesterone fluctuations particularly influence melanin production.
Genetics
Family history plays a significant role in pigmentation disorders. Some individuals are genetically predisposed to conditions like vitiligo or have inherited tendencies toward hyperpigmentation.
Medications
Certain medications, including antimalarials, chemotherapy drugs, and some antibiotics, can cause pigmentation changes as side effects.
Inflammation and Trauma
Acne, eczema, cuts, burns, and other skin injuries can trigger post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin types.
Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Skin pigmentation disorders can be broadly categorized into hyperpigmentation (excess pigment) and hypopigmentation (reduced pigment). These conditions affect millions worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life.
Common hyperpigmentation disorders include melasma, solar lentigines, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Hypopigmentation disorders primarily include vitiligo and albinism, though these are less common.
Pigmentation Treatment Options
Effective pigmentation treatment requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the specific condition and individual needs:
Topical Treatments
Hydroquinone: The gold standard for lightening hyperpigmentation
Tretinoin: Accelerates cell turnover and reduces pigmentation
Kojic acid: Natural lightening agent derived from fungi
Vitamin C: Antioxidant that inhibits melanin production
Arbutin: Gentle lightening agent suitable for sensitive skin
Professional Procedures
Chemical peels: Remove pigmented skin layers
Laser therapy: Targets specific pigmented areas
Microdermabrasion: Exfoliates surface pigmentation
IPL (Intense Pulsed Light): Treats various pigmentation types
Cryotherapy: Freezes and removes age spots
Combination Therapy
Most effective treatment plans combine multiple approaches for optimal results. A dermatologist can customize treatment based on pigmentation type, skin tone, and individual response.
Skin Pigmentation Causes and Treatment: Prevention Strategies
Prevention remains the best approach for managing pigmentation:
Daily broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30+)
Protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats
Avoiding peak sun hours (10 AM - 4 PM)
Gentle skincare to prevent inflammation
Regular dermatological check-ups
Finding the Best Dermatologist in Bangalore
When dealing with pigmentation concerns, consulting a qualified dermatologist is crucial. The Best Dermatologist in Bangalore can provide accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and monitor progress effectively.
Look for dermatologists with:
Board certification in dermatology
Experience treating pigmentation disorders
Access to advanced treatment technologies
Positive patient reviews and outcomes
Comprehensive approach to skin health
About MedStar Speciality Hospital
For expert dermatological care in Bangalore, MedStar Speciality Hospital offers comprehensive skin pigmentation causes and treatment solutions. Our experienced dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating various skin pigmentation disorders using state-of-the-art technology and evidence-based pigmentation treatment approaches.
At MedStar Speciality Hospital, we understand that each patient's pigmentation concerns are unique. Our team provides personalized treatment plans combining the latest therapeutic options with proven traditional methods to achieve optimal results.
Contact Details:
Phone: +91 9611935455 or +91 8041127524
Email: info@medstarhospital.in
Address: Medstar Speciality Hospital #641/17/1/3, Kodigehalli Main Road, Sahakarnagar, Bangalore - 560 092
Website: https://www.medstarhospital.in/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to see results from pigmentation treatment?
Most patients begin seeing improvement within 4-6 weeks of consistent treatment, though complete results may take 3-6 months, depending on the pigmentation type and severity.
2. Can pigmentation disorders be completely cured?
While many pigmentation disorders can be significantly improved or cleared, some conditions, like melasma, may recur with hormonal changes or sun exposure. Maintenance treatment is often necessary.
3. Are pigmentation treatments safe for all skin types?
Treatment safety varies by skin type and pigmentation condition. Darker skin tones require specialized approaches to avoid complications. Always consult a qualified dermatologist for personalized advice.
4. What's the difference between age spots and melasma?
Age spots are typically round, well-defined brown spots caused by sun exposure, while melasma appears as larger, irregular patches often triggered by hormonal changes and typically affects the face symmetrically.
5. Can home remedies effectively treat skin pigmentation?
While some natural ingredients may provide mild benefits, professional treatment is typically more effective and safer for significant pigmentation concerns. Home remedies should complement, not replace, professional care.







If you’re in the UK and need academic help, I’d go with an essay service uk like RoyalWriter. They have real experts across different subjects, and my experience was flawless. My psychology essay came well-researched, structured, and free of plagiarism. What I really liked was how professional yet friendly their support team was. You can message your writer directly, which makes the process transparent and easy.
The Heartbeat Clinic appreciates this insightful guide on kidney function and patient care. At our facility, we provide expert evaluation and POTS treatment through advanced services such as Metabolic Stress Testing, Echocardiography, Autonomic Nervous System Testing, EECP Therapy, and Assessment of Forearm Blood Flow. As a leading POTS treatment center in Dallas, we offer comprehensive POTS consultation, accurate POTS diagnosis, and personalized care by the best doctors for POTS treatment. Patients seeking professional, expert care for POTS choose the Best POTS Clinic for top-rated POTS treatment in Dallas. Learn more about our services at our Metabolic Stress Testing page.
Great insights on kidney health! Just like maintaining wellness requires the right expertise, growing a business online demands strategic digital solutions. At Crossway Consulting, we provide comprehensive social media marketing service, including social media marketing Dallas, email marketing Dallas TX, and SEO Services to boost visibility and engagement. Our offerings also include website design Dallas TX, PPC services for lawyers, technical SEO consultant, Android App Development, AEO Services, Enterprise SaaS Solutions, and Custom Website Designing Services. Investing in professional digital strategies ensures measurable results and long-term growth for your brand.
Great insights on health maintenance! Similarly, keeping trucks in peak condition is essential for performance and safety. Venus Truck Shop offers expert truck engine repair, truck clutch repair, and truck oil change services to prevent costly breakdowns. Their comprehensive Truck Repair Services, including truck brake repair, commercial truck AC repair, Semi Truck Repair Services, and Trailer Repair Services, ensure fleets stay reliable and road-ready. Trusted by top-rated semi truck repair shops, Venus Truck Shop combines skilled technicians, advanced diagnostics, and preventive maintenance to maximize uptime and vehicle longevity.
This is an insightful guide! Just like maintaining health is crucial, keeping your fleet in top condition is equally important. A reliable trailer repair shop or searching for trailer repair near me ensures your vehicles remain safe and efficient. Regular truck pm service from a trusted truck repair shop can prevent costly breakdowns. Texas Truck Repair offers expert commercial truck repair, truck transmission repair, and professional truck body repair and truck body work, making them a go-to choice for long-term reliability and performance.